Introduction.
The Assets, Liabilities, Equity accounts and their results make up the first attributable scope, that is, the imputations of a transaction referred to this area must always add zero (0). But the management of contingencies, for example, budget or pending orders, require other imputable areas because the imputations in each of these areas must also always add zero (0). This is defined in the AccountsPlans table ambitoimputa column.
Companies can be independent or be part of a group, move some Accounts through the PersonsAccounts relationship because each Company is a Legal Person.
The Processes table has one row for each step of these processes that are generally for information and transaction consultation; from multiannual planning, annual budgets, production, maintenance, warranty, purchase or supply programs, etc. up to sales orders and invoices, receipt reports, income receipts, proof of discharge, etc., and automatic settlements when certain criteria such as tax settlement, depreciation, valuation, inflation adjustments, year-end closures, etc., are met. All these processes and many more generate transactions and all will be typified as steps in the Processes table. The AutoTransProgram table relates the automated transaction program with Processes and Calendar, activating them when the time comes and they are authorized by a User if required. All other transactions are activated when an authorized User orders it and the necessary information is ready.
The transactions generate from 2 to thousands of compensated imputations that are recorded in the Imputations table, always measuring their value, in any national and / or virtual currency, more quantity and time if necessary. Some imputations generate or initiate a validity of an account payable or receivable, of a continuous supply of an article for several periods of time, of an item of a contract that is maintained until its objectives are met, of a reference of a production program that enters to be executed, etc., for which it decomposes into maturities, which are kept in the Valid table while they are managed, to program in time the values and quantities involved, necessary when analyzing cash flows or schedules of pending operations .
The rest goes in a single file apart from the relational tables. Blocks of information such as the details of the Processes, or the complementary data of the Transactions, the Imputations and the InForce.
The Things must correspond to the classification of products and services of the United Nations, UNThingsCatalog table and, if required, the tariff position will be in Tariff.
The Things can have 2 relations, even simultaneous with Imputations because the value of the imputation depends on the type of currency (IdMoneda) and its change, which are found in the Things and Prices tables. The other relationship can be presented when an imputation refers to a thing, but does not generate pending, for example the cost of sales of an item. It is necessary to be able to report sales costs per item.
The Persons table can be directly related to the Imputations table when it is a movement that does not generate pending in the InForce table, examples: a cash sale. It is necessary to be able to report sales per customer, including cash.
The Imputations can be related to records of the same table as in the case of the imputation generated by an account receivable and the imputations that pay that debt.
The Companies can be part of more or less complex conglomerates, their national tax unit defines a level of accounting, but it is necessary to subdivide for the local tax, so that the accounting allocations must be detailed at least at the level of the accounts that affect, but may be more detailed as in the case of inventories that require defining the dependency, warehouse, shelf, row and height, or warehouse, in which they are located. IBMSYS allows all the detail that is required without ceasing to define the level of accounting and consolidation levels thanks to the fact that the Companies table has a tree structure where the root corresponds to the maximum business consolidation with the possibility of also consolidating the branches or sub-branches that are wanted, establish the level of accounting at will and detail the dependencies without restriction. The sheets will be the most detailed subdivisions.
Several tables have a tree structure: Locations, Companies, Categories, AccountPlans, Things, UNThingsCatalog, Tariff, Processes, Roles and Norms. Accounts has no own tree structure, but inherits AccountPlans.
To ensure that the accounting charges can discriminate more than the accounts, the Table of Imputations inherits the Company to account for Accounts, but may have a more detailed one, to specify the dependency affected within the same Company.
The Imputations table is the one that has the most relations to facilitate the consultation of the detailed history and what is pending in its InForce dependent table.
The following diagram shows the additional relationships of the Companies table with the other tables. The Accounts are related to Companies at Legal Entity level subject to the administration of national taxes or lower if it is required to detail to be able to declare local taxes or because senior management decides, for which different levels of Things can also be established and Imputations Roles and Processes can define other convenient levels including conglomerates of Legal entities. All levels can be consolidated.
Carlos
Marx envisioned that accounting would be increasingly important for
business management. In Volume II of Capital, Chapter IV Circulation
expenses, in numeral 1. b), it defines: “… Accounting, on the
other hand, as an ideal control and compendium of the process, is
more necessary the more social character this process acquires and
more loses its purely individual character; it is more necessary,
therefore, in capitalist production than in the scattered production
of artisanal and peasant enterprises, and more necessary still in
collective production than in capitalist production. ”
Our
intelligent business management system (IBMSYS) requires that all
economic information be qualified by accounting concepts, contained
in the account plan, and that its registration and evidence be made
only as accounting transactions. With this we can achieve that
"control and ideal compendium of the process" is total,
using the necessary contingent and control accounts. As a result, a
minimum of related information entities and a minimum of algorithms
to be programmed are achieved.
The
implementation and updating of current business management systems
(ERP, CRM, SCM, etc.) requires titanic efforts because the cost and
time involved and the chances of failing in the attempt traumatize
the adequacy of companies to new technologies of information and
telecommunication and the progress of international trade. To
guarantee the success of these efforts, a small number of highly
specialized consulting firms have been accredited, in exchange for
rising costs and user dependence.
A
simplified system is required that, due to the advanced synthesis of
administrative theory, is more concise but deeper than current
systems, achieving its easy understanding by the technicians and
professionals in charge of business support areas so that They can
implement and update it, preferably directed by the Quality
Management Department, with the unrestricted support of senior
management. The implementation and updating of business management
systems should cease to be the privilege of highly specialized
external consultants.
System
oriented norrms-based processes.
Process-oriented
business management has managed to close the gap between theory and
business reality. The need to offer customers products according to
their specifications or expectations and to maintain uniformity in
the products or services of the same reference motivated the
emergence of control, monitoring and quality management, It was a
great success of the International Organization Standardization (ISO)
manage to synthesize these theories in ISO 9000 because in a few
decades it has been implemented in the vast majority of important
human companies.
Companies
implement it massively to improve production, achieve recognition and
facilitate distribution. They should also implement ISO 14001,
environmental management and ISO 45001, occupational health and
safety management. Companies that have any relationship with human or
animal feed should implement ISO 22001 for food safety management,
etc. Towards the future the tendency is to continue simplifying these
norms because their success has been due in large part to the fact
that they managed to synthesize administrative theories, varied and
contradictory at times, simplifying the creation of the global
business network, taking advantage of the evolution of the
technologies of information and communication, so that we reach the
predominance of online commerce.
Accounting
as a tool for conceptualization, registration and control of economic
information.
The
vision of accounting as the mental image of the production process
has great flaws in the current practice of business management
systems, insisting on making separations derived from the tendency of
accounting managers to limit their scope. With the new systems the
accounting offices tend to disappear; accounting criteria of the
administrators is required for the control and analysis of the
information, the accounting record work is done automatically. It
should not be allowed to consider some economic management
registration systems as complementary or parallel to the accounting
systems, use of the order accounts to involve them using the
contingent and control accounts.
Expert
system for implementation.
ISO
9001 applies to all types of companies, the design and development of
products and services is optional because there are companies that
buy to sell without transforming, such as shops and service
commissioners, others add some of their own complementary products or
services, and Many must be designing and developing in order to stay
in the market. ISO 9001 can be applied to the entire business
structure, the other norms clarify or add other specific controls.
By
investigating, we will build a tree of possible implementations in
such a way that, as it grows, it is more times that we will find a
product ready to implement than the need to create new branches and
sub-branches to satisfy a new type of Company. Interviewing the
experts of the interested Company, in order to locate it in the
implementations tree, can be replaced by access to the already
registered information of that company in government or union
censuses, tax returns, and records of purchase, sale and production
declared. A government committed to standardization and
simplification could well request all the necessary data for a rapid
implementation of the IBMSYS. Thus we could evolve to expert systems
and then to intelligent machines of implementation.
Transactional
expert system.
The
business operation generates instances of predefined processes that
combine information analysis and action decisions, when the
information is completed and authorization exists, the system can
automatically decide on an action. The actions can be of a single
instant, like receipt of payments to an invoice or automatic
liquidation of a depreciation, or they can initiate an operation that
involves other multiple steps such as a credit sale or an automatic
production order. In all cases, one or more offset sets of accounting
charges are generated that optionally affect contingent accounts,
such as annual sales budget or pending orders, and inventory accounts
and their results (Assets, Liabilities, Equity, income and expenses
of a period ). The affectation of Persons and Things
can be determined by the accounts of the Asset, of the Liability, of
the Patrimony or of the Debtor and credit contingencies involved.
The
steps of the processes that imply an economic change contain
descriptions, acronyms, format of the Form of visualization and
capture of complementary data, format of the Report for printing and
to store the complete transaction, and data of defined occurrence for
each type of document that detail how forms, reports and imputations
are generated. This will allow the creation of information trees to
know how known information should be displayed and unknown
information should be requested, how it should be accounted for and
how the transaction evidence document should be constructed. That
algorithm would be the core of the transactional expert system and
would use previous data plus those supplied by the user, flags of the
affected accounts and indicators of special deals. Specific
algorithms by type of transaction would be terminated and new types
of transactions could be added creating the step in the corresponding
process, without increasing the code.
The
preparation of interactive transactions must allow the procedure to
be suspended, without losing the advance, when the user requires it,
a transaction must be able to be prepared in more than one session
and, in some cases, it must be able to be delegated to another user
and also be able to collaboratively do between Multiple users For
example, the preparation of the annual budget should involve the
administrators of the different dependencies of the Company.
Simultaneously several users must be able to be working on the
budget, each in their area. Once these steps have been completed, the
preparation must be transferred to a budget consolidation committee
and the members of this committee must be able to work in all areas
until the consensus is approved by this committee, and later by the
senior management.
Let's
look at the general system flowchart:
The
System Database
The
data necessary to manage companies seek to meet the needs of all
types of ventures. Proprietary systems such as SAP, mixed as Odoo and
open and free software as Idempiere have been implemented in hundreds
of thousands of Companies. But its databases are very complicated,
Idempiere has more than 800 tables with many relationships that
hinder their understanding and restrict potential volunteers to
improve the code. Odoo has more than 100 that is 8 times more
synthesized in its data than Idempiere. Our IBMSYS system has 26
tables, 4 times more synthesized than Odoo. How was it possible to
simplify so much? Using the possibilities of the order accounts it is
possible that all the economic information is recorded in accounting
and it is also possible to have a unique algorithm to process all
possible transactions in any type of company.
Let's
see how a database with 26 tables replaces the 832 of Idempiere and
the 107 of Odoo without losing information. This is achieved by
preserving the necessary entities to relate the information of
Persons things and concepts,
plus the information to control access to the system, the definition
of productive and administrative processes and the registration of
transactions. The rest of the information, specific to each type or
subtype of transaction, is accessed only through some register or
tuple of the relational entities, so those can be in a single file,
which we could call Add-ons, managed in relative shortcut the
structures of that information, the initial direction of recording
and reading and the size. Robust database managersii
support this type of add-ons as part of the logical transaction,
allowing the consistency of the information to be maintained, even in
the event of a System crash. Thus, a simplified relational design and
higher operating speed are achieved, and a variable design with which
we can modify the structure of some data without modifying the code.
The definition of the different complementary data needs by type of
transaction is established and processed as additional information of
a single unaltered algorithm, both for known types and for those
derived from improvements or expansion of operations. The management
of variable data in business was synthesized.
Let us see in a diagram the 26 tables with the necessary relations to easily access the information, except for the relations of the Companies table with the other tables shown in another diagram.
ER diagram, IBMSYS relational database:
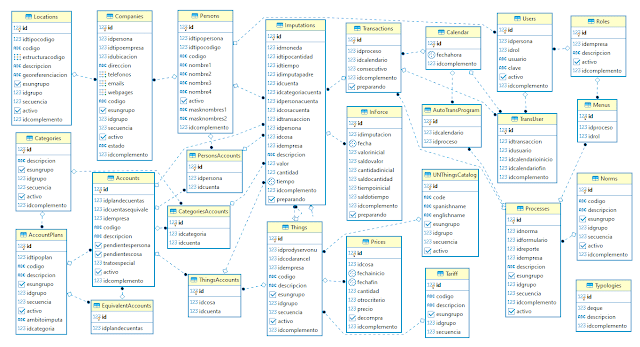
Let us see in a diagram the 26 tables with the necessary relations to easily access the information, except for the relations of the Companies table with the other tables shown in another diagram.
ER diagram, IBMSYS relational database:

It is only necessary to establish the
geographical locations of the Companies and their
different dependencies, because that is where the Persons
work, the third parties are served and Things are
located.
Persons who establish business relationships begin to act as Companies. A Person may be related to one or more Companies, may serve as one or more IBMSYS Users. Each User can perform one or more Roles, totally or partially, according to the assignment of tasks of the personnel plant and the restrictions that the bosses can define.
Persons who establish business relationships begin to act as Companies. A Person may be related to one or more Companies, may serve as one or more IBMSYS Users. Each User can perform one or more Roles, totally or partially, according to the assignment of tasks of the personnel plant and the restrictions that the bosses can define.
Each
Role can perform one or more steps of the Processes through Menus
where those options are shown, pending issues and dashboards that
summarize how the role is being played.
The
Processes should correspond to the Norms that
are applied in the Company, such as quality, environmental, labor,
etc.
Persons
related to the Company affect one or more accounts and an account may
be affected by one or more Persons, this is expressed with the
PersonsAccounts table that are related to the Persons
and Accounts tables; Examples: Partners, Workers, Customers,
Suppliers, Competitors, etc. Similarly, the ThingsAccounts
table relates the Things and Accounts tables; Examples:
Raw materials, merchandise, consumer items, fixed assets, logistic,
financial, processing services, etc. Things have purchase and
sale Prices that vary with time and other
circumstances.
Sometimes
it is necessary to see the accounting information grouped
transversely, examples: Analysis of income and expenses by cost
center or by consolidated projects that can group many products and
services, for this we use the Categories table with 2
possibilities: related to the Accounts by table the
CategoriesAccounts table, when it is required to analyze
information of a lower level than defined in the Account Plans or
Categories directly related to the AccountsPlans table. This
relationship can be complemented by business dependence. With these
relationships and taking into account that the historical accounting
movement is in Imputations and InForce
tables, times and amounts currently pending are in force, financial
reports and dashboards can be produced.
The Assets, Liabilities, Equity accounts and their results make up the first attributable scope, that is, the imputations of a transaction referred to this area must always add zero (0). But the management of contingencies, for example, budget or pending orders, require other imputable areas because the imputations in each of these areas must also always add zero (0). This is defined in the AccountsPlans table ambitoimputa column.
Companies can be independent or be part of a group, move some Accounts through the PersonsAccounts relationship because each Company is a Legal Person.
Governments,
or custom, define Account Plans that Companies must use and,
how it is possible for a group of Companies to operate in
different countries, it is necessary to be able to present the same
accounting information classified according to different account
plans, which can be achieved using the EquivalentAccounts
table.
The Processes table has one row for each step of these processes that are generally for information and transaction consultation; from multiannual planning, annual budgets, production, maintenance, warranty, purchase or supply programs, etc. up to sales orders and invoices, receipt reports, income receipts, proof of discharge, etc., and automatic settlements when certain criteria such as tax settlement, depreciation, valuation, inflation adjustments, year-end closures, etc., are met. All these processes and many more generate transactions and all will be typified as steps in the Processes table. The AutoTransProgram table relates the automated transaction program with Processes and Calendar, activating them when the time comes and they are authorized by a User if required. All other transactions are activated when an authorized User orders it and the necessary information is ready.
The transactions generate from 2 to thousands of compensated imputations that are recorded in the Imputations table, always measuring their value, in any national and / or virtual currency, more quantity and time if necessary. Some imputations generate or initiate a validity of an account payable or receivable, of a continuous supply of an article for several periods of time, of an item of a contract that is maintained until its objectives are met, of a reference of a production program that enters to be executed, etc., for which it decomposes into maturities, which are kept in the Valid table while they are managed, to program in time the values and quantities involved, necessary when analyzing cash flows or schedules of pending operations .
The rest goes in a single file apart from the relational tables. Blocks of information such as the details of the Processes, or the complementary data of the Transactions, the Imputations and the InForce.
The Things must correspond to the classification of products and services of the United Nations, UNThingsCatalog table and, if required, the tariff position will be in Tariff.
The Things can have 2 relations, even simultaneous with Imputations because the value of the imputation depends on the type of currency (IdMoneda) and its change, which are found in the Things and Prices tables. The other relationship can be presented when an imputation refers to a thing, but does not generate pending, for example the cost of sales of an item. It is necessary to be able to report sales costs per item.
The Persons table can be directly related to the Imputations table when it is a movement that does not generate pending in the InForce table, examples: a cash sale. It is necessary to be able to report sales per customer, including cash.
The Imputations can be related to records of the same table as in the case of the imputation generated by an account receivable and the imputations that pay that debt.
The Companies can be part of more or less complex conglomerates, their national tax unit defines a level of accounting, but it is necessary to subdivide for the local tax, so that the accounting allocations must be detailed at least at the level of the accounts that affect, but may be more detailed as in the case of inventories that require defining the dependency, warehouse, shelf, row and height, or warehouse, in which they are located. IBMSYS allows all the detail that is required without ceasing to define the level of accounting and consolidation levels thanks to the fact that the Companies table has a tree structure where the root corresponds to the maximum business consolidation with the possibility of also consolidating the branches or sub-branches that are wanted, establish the level of accounting at will and detail the dependencies without restriction. The sheets will be the most detailed subdivisions.
Several tables have a tree structure: Locations, Companies, Categories, AccountPlans, Things, UNThingsCatalog, Tariff, Processes, Roles and Norms. Accounts has no own tree structure, but inherits AccountPlans.
To ensure that the accounting charges can discriminate more than the accounts, the Table of Imputations inherits the Company to account for Accounts, but may have a more detailed one, to specify the dependency affected within the same Company.
The
TransUser table is a log of the Users for each session,
with start and end dates, in which they acted preparing Transactions.
The Imputations table is the one that has the most relations to facilitate the consultation of the detailed history and what is pending in its InForce dependent table.
The following diagram shows the additional relationships of the Companies table with the other tables. The Accounts are related to Companies at Legal Entity level subject to the administration of national taxes or lower if it is required to detail to be able to declare local taxes or because senior management decides, for which different levels of Things can also be established and Imputations Roles and Processes can define other convenient levels including conglomerates of Legal entities. All levels can be consolidated.
Conclusions
It
is possible to create an Intelligent Business Management System based
on an advanced synthesis of business information. First: using only
the accounting for the economic registry, the order accounts are used
to register the assets of third parties that the company manages and
to include all contingencies, and second by typing all business
economic transactions in a single Entity, to store its formats of
forms and reports, how they are filled out and how they are accounted
for.
Transactions
generate offset debit and credit accounting movements (Imputations)
that can be a minimum of 2 to thousands. An accounting movement can
start a scheduled process (InForce) with maturities by values,
amounts or time, whose breaches generate corrective or penalties. So
the pending to manage begins with a generator event as the parent of
the events of its development.
Business
management processes are framed in international norms, with ISO 9001
as a universally accepted reference, so that the other norms are
complements to manage specific controls. Process management should be
based on information for decision making and the activation of
transactions that can be automated in large part, allowing only very
justified changes, based on experience and strictly audited in order
to promote continuous improvement, without losing the connection with
the already registered. Authorized users assume roles that are
defined as the ability to execute a subset of options to inform and
activate transactions. There will be more and more automaton users
that must be supervised by human beings.
Once
the IBMSYS has been developed and tested, implementation can be
facilitated in companies that currently use ERP / CRM / SCM systems
and others, by programming automatic conversions based on the work of
groups of researchers studying current systems such as SAP, COMPIERE
and their derivatives, ODOO, etc., in such a way that part of the
current code of these systems may become IBMSYS data.
The
information recorded would simply change format and can make
migration almost transparent to users. A new database to help future
implementations will be extracted from what the research groups of
the old systems synthesize, in addition to the qualitative record in
the new implementations and migrations, which will mature an expert
system that in the future could Implement almost automatically,
acting as an intelligent machine.
Research
groups for the migration of old to new systems should specialize for
each product and possibly in certain types of companies. For example,
in the Universities you can promote groups of researchers studying
current systems in related areas such as: the oil and mining sector,
the government sector, the industrial sector, the commercial sector,
the health sector, the financial sector, etc. , detailing according
to the scope of the systems implemented, with the possibility of
consolidating models by their common processes.
Once
the IBMSYS has been implemented in a company, it would be advisable
to allow the operation in parallel with the previous systems for a
reasonable time, transferring the daily changes and movements in
automated batch processes, first from the current system to the new
one and then the new one to the replaced one.iii
iHernan
Pardo is developing business software since 1969. He was trained as
a Software Engineer by IBM in Bogota. You can see a summary in
spanish of his professional life and his proposal in this blog post:
https://hernanpardosilva.blogspot.com/2019/03/nueva-teoria-para-crear-el-sistema-la.html
iiAlibaba
Cloud provides services for most of the SQl and NoSQL database
managers. For example, Postgresql
is indicated for the IBMSYS database because it is robust and
handles Large Objects that serve to store the required Add-ons,
preserving the integrity of the logical transaction even in case of
falls and recovery. See:
https://www.alibabacloud.com/product/apsaradb-for-rds-postgresql
iiiThe
most convenient processing now for business management systems is
SaaS (Software as e service) given the reliability and agility
provided by large cloud services. See:
https://www.alibabacloud.com/knowledge/what-is-saas
The trend of enterprise
software is on the one hand towards integration, but is still called
ERP includes CRM and other supplements, on the other hand local
systems give way to Saas cloud. See:
https://www.cloudmasters.es/un-pequeno-analisis-de-la-decada-en-lo-referente-a-cloud/
“What is an ERP: Complete guide to choose
the best ERP of 2019”:
https://papelesdeinteligencia.com/que-es-un-erp/


